Objections are a natural part of the sales process. When potential prospects express concerns or hesitations, it is not a signal to end the conversation but an opportunity to understand their needs and address them effectively.
SDRs who master the art of overcoming objections are better equipped to build trust and close deals.
To effectively overcome objections during cold calls, it is crucial to listen actively and empathize with the prospect. By acknowledging their concerns and demonstrating an understanding of their perspective, sales representatives can create a constructive dialogue.
This approach allows for the identification of the underlying issues driving the objections, enabling a more targeted and effective response.
Developing a comprehensive strategy for handling objections involves a combination of preparation, effective communication, and adaptability. Sales representatives who prepare for common objections can respond confidently and accurately.
Clear communication, tailored to the prospect’s specific needs and concerns, helps dismantle objections. Being adaptable ensures that unforeseen objections can be managed effectively, keeping the conversation moving toward a resolution that benefits both the prospect and the sales representative.
Understanding Objections in Sales
When engaging in cold call calls, SDRs can expect objections as a natural part of the decision-making process. It is essential to comprehend the nature of these objections to effectively address them.
Psychology Behind Objections
- Risk Aversion: Prospects may object due to the fear of making a wrong decision.
- Status Quo Bias: A preference for the current state of affairs may cause objections as the prospect avoids change.
- Misunderstanding: Lack of information or misconceptions can result in objections.
- Trust Issues: Without trust in the salesperson or the company, objections are more likely to occur.
Understanding the types of objections and the psychology behind them allows for tailored responses that address the specific concerns of each prospect.
Preparing to Handle Objections
Successfully overcoming objections in cold calls begins with thorough preparation, which involves meticulous research and rehearsing objection handling through role-play scenarios.
Research and Preparation
Before engaging in a sales call, one must have a deep understanding of the product or service being offered. This includes knowing the:
- Features: List out what the product/service does.
- Benefits: Clearly outline how these features translate into tangible results for potential prospects.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Identify what sets the product/service apart from competitors.
In addition to product knowledge, one must research the potential prospect. Create a prospect profile detailing:
- Industry: Understand the needs and challenges specific to the client’s industry.
- Company Size: Tailor communication style and solution scale accordingly.
- Decision Makers: Know who will be on the call and what their main concerns might be.
SDRs should also anticipate common objections. Utilize a table format to categorize and strategize:
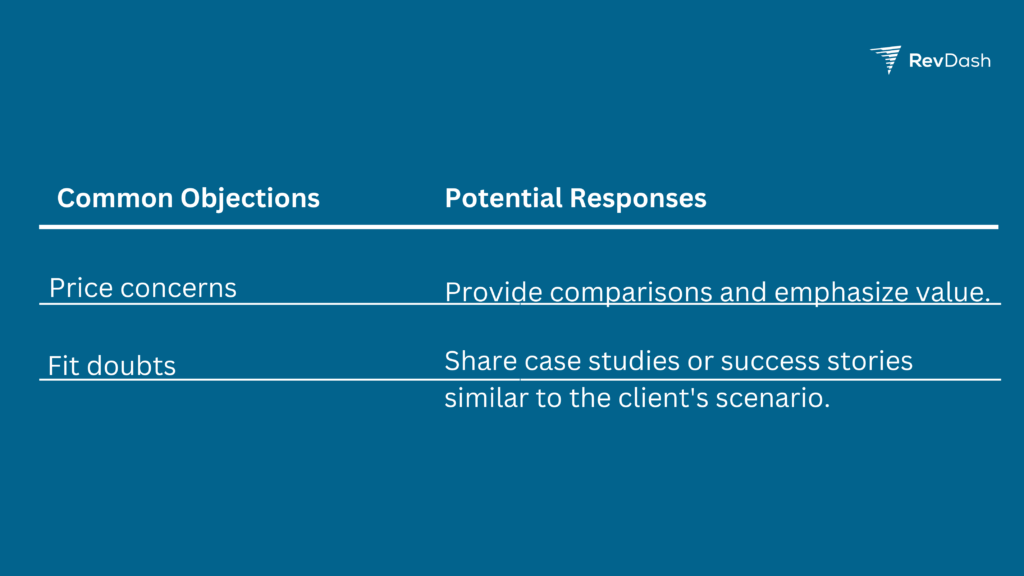
Role-Playing and Practice
After research, salespersons must hone their skills in handling objections through role-playing exercises. Practice allows them to:
- Have a set of responses ready to address common and unique objections.
- Develop the ability to think on their feet and adapt to unforeseen challenges.
During role-play:
- Participants should switch roles between sales representative and prospect to gain multiple perspectives.
- Realism: Incorporating realistic scenarios that mirror past cold calls for more effective practice.
- Feedback: Constructive criticism should be shared post-role-play to improve performance.
Effective Techniques for Overcoming Objections
In cold calls, success hinges on addressing client concerns effectively. These techniques are designed to break down barriers and foster a constructive dialogue that moves the sales process forward.
Active Listening Skills
Active listening is pivotal. It involves more than just hearing words; one must understand the message behind the objection. Sales professionals should:
- Reflect: Paraphrase what the client says to show understanding.
- Clarify: Ask questions to get to the core of the concern.
- Acknowledge: Validate their feelings without immediately jumping to a solution.
Empathy and Reassurance
Empathy builds trust. When salespeople demonstrate they comprehend a client’s viewpoint, it creates rapport. Techniques include:
- Using phrases like: “I understand where you’re coming from…” to show empathy.
- Reassurances: Assuring the client their concerns are valid and will be addressed.
Solution-Oriented Responses
Once concerns are fully understood, it’s crucial to respond with tailored solutions. Salespeople should:
- Provide Specifics: Give concrete examples of how a product/service solves their particular issue.
- Highlight Benefits: Connect the features of an offering to the client’s needs.
By integrating these methods into cold calls, SDRs can transform objections into opportunities.
Sealing the Deal
In the final stages of a cold call, successfully overcoming objections can lead to sealing the deal. This part involves ensuring the prospect feels understood and using proven closing techniques.
Confirming Understanding
Before attempting to close a sale, it’s imperative to verify that the prospect’s concerns and objections have been fully addressed. They should feel heard and validated.
- Summarize Key Points: Briefly summarize the main points of agreement to demonstrate comprehension.
- Ask for Feedback: Pose direct questions like, “Have I addressed all of your concerns?” to invite any final clarifications.



