One of the major challenges SDRs face when sending cold emails is the risk of their emails being flagged as spam, which often leads to getting deleted without ever reaching the prospect. So how to avoid your cold email ending up in spam?
The algorithms that filter emails are increasingly sophisticated, yet understanding how they work can greatly increase the chances of an email landing in the inbox.
To ensure that a cold email reaches its target, it is essential to write it with care, sticking to certain best practices that signal to spam filters the legitimacy of the email. From the subject line to the closing signature, every component of an email can influence its deliverability.
Crafting clear, concise, and relevant content without the overuse of sales language can result in a higher rate of successful email delivery.
Avoiding spam triggers, personalizing emails for each recipient, and maintaining a professional tone are just a few of the techniques that can help an email find its way to the intended inbox rather than the spam folder.
Understanding Email Filters
Email filters are critical gatekeepers, determining if an email lands in an inbox or a spam folder. They use sophisticated algorithms to analyze incoming messages on various fronts.
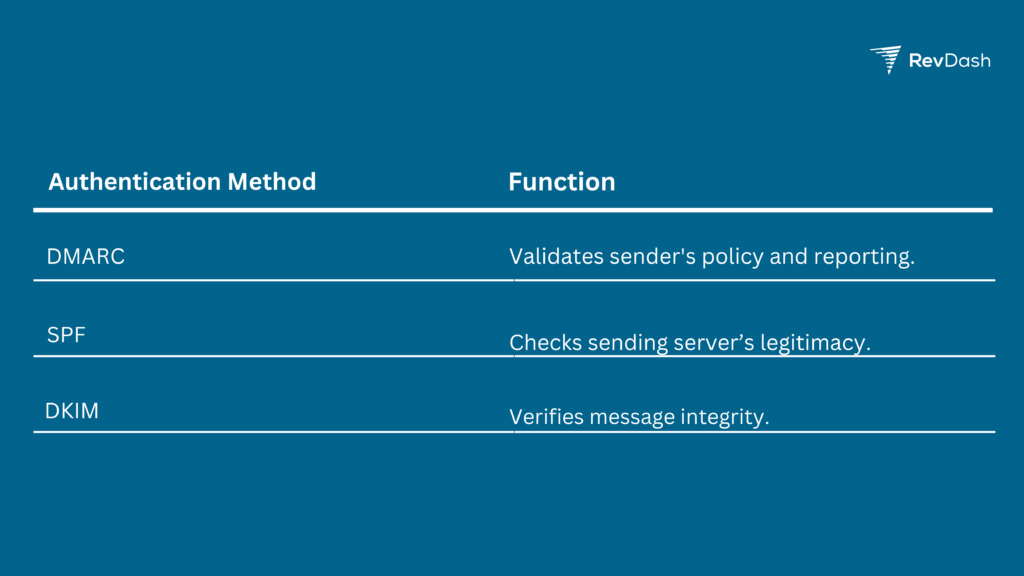
Email Authentication Methods
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC), Sender Policy Framework (SPF), and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) are key in verifying sender identity.
A properly configured DMARC with SPF and DKIM records significantly lessens the likelihood of emails being marked as spam. They ensure that the email is sent from an authorized domain and hasn’t been tampered with during transit.
User Engagement Metrics
Filter algorithms pay close attention to how recipients interact with previous emails from the sender. High levels of engagement typically signal to filters that the sender’s emails are welcome. Important metrics include:
- Open rates: how often emails are opened.
- Click-through rates: how frequently links within the emails are clicked.
- Reply rates: the rate at which recipients respond to emails.
Low engagement can alert filters to potential spam, leading to future emails being filtered out.
Content Analysis
Content analysis entails scrutinizing the email’s subject line and body for triggers that might classify it as spam. Filters examine for:
- Keywords: Certain words or phrases are strongly associated with spam.
- Links: Emails containing links to suspicious domains are prone to filtering.
- Attachments: Unexpected or executable file types may set off alarms.
Emails should use clear, concise language, and maintain relevance to avoid being flagged by content algorithms.
Crafting the Email
Properly crafting an email significantly reduces the chances of it being marked as spam. Attention to detail such as customization and relevant content plays a critical role.
Personalize Your Content
Email personalization begins with using the recipient’s name and referencing specific interests or needs they may have. Personalization tactics include:
- Segmentation: Separating email lists based on subscriber demographics or activities.
- Tailored Messaging: Crafting messages that resonate with individual recipients or segmented groups.
Compelling Subject Lines
The subject line is an email’s first impression, and it should be:
- Clear and Direct: Reflect the content of the email without misleading the recipient.
- Avoiding Spam Triggers: Steer clear of words frequently flagged by spam filters, such as ‘free,’ ‘guarantee,’ and ‘no risk.’
Relevant Body Copy
The body of the email should deliver on the promise of the subject line with:
- Value Proposition: Explain succinctly why the message is relevant to the recipient.
- Proper Formatting: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and bold text for emphasis to improve readability.
Technical Considerations
When crafting a cold email, several technical aspects should be addressed to minimize the risk of landing in the spam folder. These include adopting respectful sending practices, using links properly, and carefully choosing language to avoid spam triggers.
Respectful Sending Practices
When sending emails, one must conform to Internet protocol standards to foster trust with the recipient’s email server. This includes:
- Authentication: Ensure that emails are sent from a server with proper SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance) records to verify the sender’s identity.
- Volume: Gradually build sending volume to establish a reputation. Sending large quantities of email suddenly can look suspicious to spam filters.
- Engagement Tracking: Monitor how recipients interact with emails sent and adapt strategies accordingly. High rates of engagement (opens and clicks) can positively affect the sender’s reputation.
Proper Link Usage
Including links in an email are common practice, but they must be used judiciously:
- Reputable URLs: Only include links from well-established and trustworthy domains.
- Display URL vs. Destination: The visible link text should match the actual URL to avoid misleading recipients.

Avoiding Trigger Words
Certain words and phrases in emails can activate spam filters. They should:
- Be Specific: Generic phrases like “Click here!” can be suspect. Instead, use specific call-to-actions related to the email’s content.
- Avoid Overuse: Words associated with sales pitches or urgency, such as “guarantee,” “risk-free,” or “instant,” should be used sparingly, if at all.
Monitoring and Improving
Effective cold email campaigns require continuous oversight and adjustments to steer clear of spam filters. Monitoring metrics and conducting tests are essential to maintain high deliverability rates.
Regularly Check Spam Folders
It is crucial to routinely inspect spam folders for cold emails that may have been mistakenly classified as spam. Request that a segment of recipients check their spam folders and mark any legitimate emails as “Not Spam.” This can help improve the sender’s reputation with email providers.
Monitor Email Deliverability
To gauge the success of an email campaign, one should track deliverability rates using tools that provide detailed reports on emails that reach the inbox, land in spam, or fail to be delivered. Vital metrics include:
- Open rates: The percentage of emails opened by recipients.
- Click-through rates (CTR): The frequency with which links within the email are clicked.
- Bounce rates: The rate of emails that could not be delivered to the recipient’s inbox.
A/B Testing Strategies
Employ A/B testing to hone in on the most effective email elements:
- Subject lines: Compare different subject lines to see which yields a better open rate.
- Email content: Test various formats and messages to identify what resonates best with readers.
- Sending times: Send emails at different times to determine when recipients are most likely to engage.
By making improvements based on real-time feedback and data, one can significantly diminish the odds of cold emails being relegated to spam.



